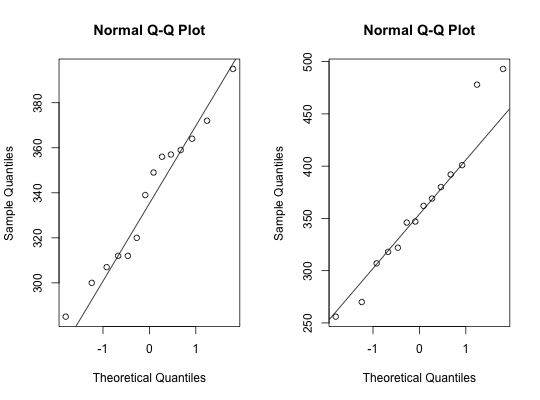
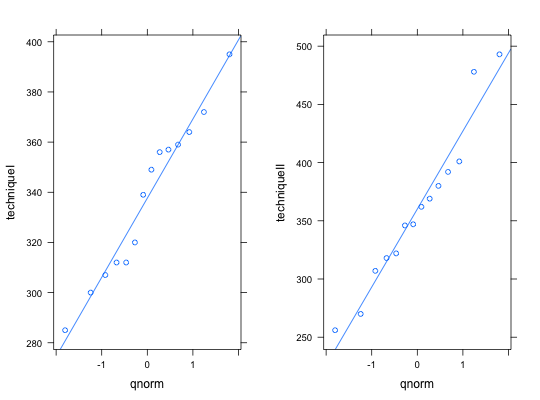
Silicon Chips
Two techniques of splitting chips are randomly assigned to 28 sheets so that
each technique is applied to 14 sheets. The values recorded in Chips
are the number of usable chips from each silicon sheet.
Format
A data frame with 14 observations on the following 2 variables:
- techniqueI
number of usable chips
- techniqueII
number of usable chips
Source
Ugarte, M. D., Militino, A. F., and Arnholt, A. T. (2008) Probability and Statistics with R. Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Examples
par(mfrow = c(1, 2)) with(data = Chips, qqnorm(techniqueI)) with(data = Chips, qqline(techniqueI)) with(data = Chips, qqnorm(techniqueII))with(data = Chips, qqline(techniqueII))par(mfrow=c(1, 1)) # Trellis Approach graph1 <- qqmath(~techniqueI, data = Chips, type=c("p", "r")) graph2 <- qqmath(~techniqueII, data = Chips, type=c("p", "r")) print(graph1, split=c(1, 1, 2, 1), more = TRUE)print(graph2, split=c(2, 1, 2, 1), more = FALSE)rm(graph1, graph2)